· Kalpa Madhushan · devops · 3 min read
Mastering NFS in Linux: Setup, Mounting, Management & Troubleshooting
Learn how to configure Network File System (NFS) in Linux environments, including server setup, client mounting, persistent configurations, and common troubleshooting techniques.
🔗 Mastering NFS in Linux: Setup, Mounting, Management & Troubleshooting
NFS (Network File System) is a powerful way to share files between Linux systems over a network. This guide will walk you through:
- How NFS works
- Server-side configuration
- Client-side mounting (including multiple clients)
- Making mounts persistent
- Useful commands and tools
- Troubleshooting tips
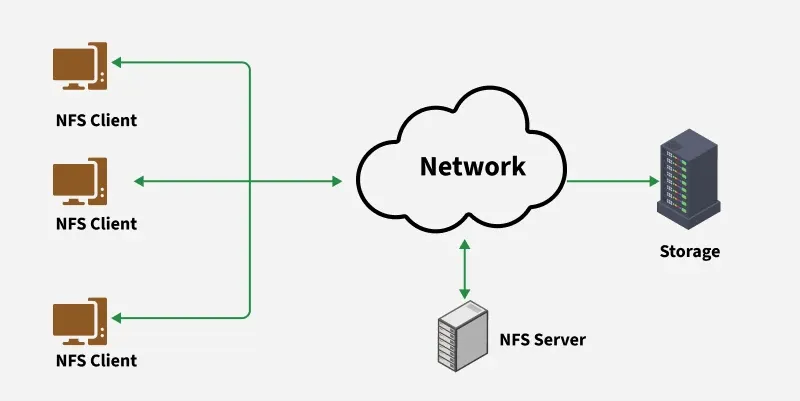
🧠 What is NFS?
NFS allows a Linux server to share directories with other Linux machines (clients) over the network. Clients can mount these directories and access them like they are part of their own filesystem.
🛠️ Part 1: NFS Server Setup
Let’s assume your NFS server has the IP 192.168.1.100.
✅ 1. Install NFS Server
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server✅ 2. Create a Shared Directory
sudo mkdir -p /srv/nfs/shared
sudo chown nobody:nogroup /srv/nfs/shared✅ 3. Configure /etc/exports
Open the exports file:
sudo nano /etc/exportsAdd this line to share with all clients in subnet 192.168.1.0/24:
/srv/nfs/shared 192.168.1.0/24(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)✅ 4. Apply Export Changes
sudo exportfs -ra✅ 5. Start and Enable NFS Service
sudo systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server
sudo systemctl enable nfs-kernel-server🖥️ Part 2: Mounting NFS on Clients (e.g., 192.168.1.101, 192.168.1.102)
✅ 1. Install NFS Client
sudo apt install nfs-common✅ 2. Create Mount Point
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/shared✅ 3. Mount the NFS Share
sudo mount 192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/shared /mnt/sharedNow, you can access /mnt/shared as if it’s a local folder.
🔁 Mounting on Multiple Clients Simultaneously
Run the same installation + mount steps on each client machine (192.168.1.101, 192.168.1.102, etc.), or use a script like this:
#!/bin/bash
MOUNTPOINT="/mnt/shared"
SERVER="192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/shared"
mkdir -p "$MOUNTPOINT"
mount "$SERVER" "$MOUNTPOINT"You can deploy this with SSH, Ansible, or by login script.
📌 Making NFS Mount Persistent (Fstab Method)
Add this line to /etc/fstab on the client machine:
192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/shared /mnt/shared nfs defaults 0 0Then test:
sudo mount -a🧾 Useful NFS Configuration Files
| File | Purpose |
|---|---|
/etc/exports | Define NFS shares on server |
/etc/fstab | Define persistent mounts on client |
/var/lib/nfs/ | Stores internal NFS state |
/etc/hosts.allow / .deny | Optional host-based access control |
🛠️ Essential Commands for NFS
| Command | Description | |
|---|---|---|
exportfs -ra | Re-export all shares | |
showmount -e 192.168.1.100 | View available exports from a server | |
mount -t nfs ... | Manually mount an NFS share | |
umount /mnt/shared | Unmount an NFS share | |
| `df -h | grep nfs` | Show mounted NFS shares |
findmnt -t nfs | Show NFS mounts in tree format | |
systemctl status nfs-kernel-server | Check NFS server status | |
sudo exportfs -v | Show active exports and settings |
🧯 NFS Troubleshooting Tips
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| ❌ Permission denied | Check /etc/exports and use correct rw options |
| ❌ Stale file handle errors | Unmount and remount, or restart NFS on client |
| ❌ Mount hangs or fails | Check firewall, NFS server status, nfs-common installed |
| ❌ Not mounted at boot | Use correct syntax in /etc/fstab, and use IP, not hostname |
❌ No export shown on showmount | Restart NFS server and recheck /etc/exports |
⚙️ Optional: Autofs (On-Demand Mounting)
If you want shares to mount only when accessed, install autofs:
sudo apt install autofsThen configure /etc/auto.master:
/mnt/nfs /etc/auto.nfsThen create /etc/auto.nfs:
shared -rw,soft,intr 192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/sharedRestart autofs:
sudo systemctl restart autofsNow, accessing /mnt/nfs/shared will trigger automatic mount.
✅ Summary
- Use
/etc/exportsto define NFS shares. - Clients can mount shares manually or via
/etc/fstab. - Tools like
showmount,findmnt, anddfhelp monitor NFS. - Automate and scale across multiple clients via scripts or Ansible.
- Ensure correct subnet (
192.168.1.0/24) permissions are in place.
🧩 Example Network Layout
| Hostname | Role | IP Address |
|---|---|---|
nfs-server | NFS Server | 192.168.1.100 |
client01 | NFS Client | 192.168.1.101 |
client02 | NFS Client | 192.168.1.102 |
All clients mount:
192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/shared → /mnt/shared



